Are you a US healthcare professional?
INDICATION
RYTELO® (imetelstat) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with low- to intermediate-1 risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) with transfusion-dependent anemia requiring 4 or more red blood cell units over 8 weeks who have not responded to or have lost response to or are ineligible for erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESA). See more
Discover how RYTELO
may work in LR-MDS

Telomerase in LR-MDS
View content
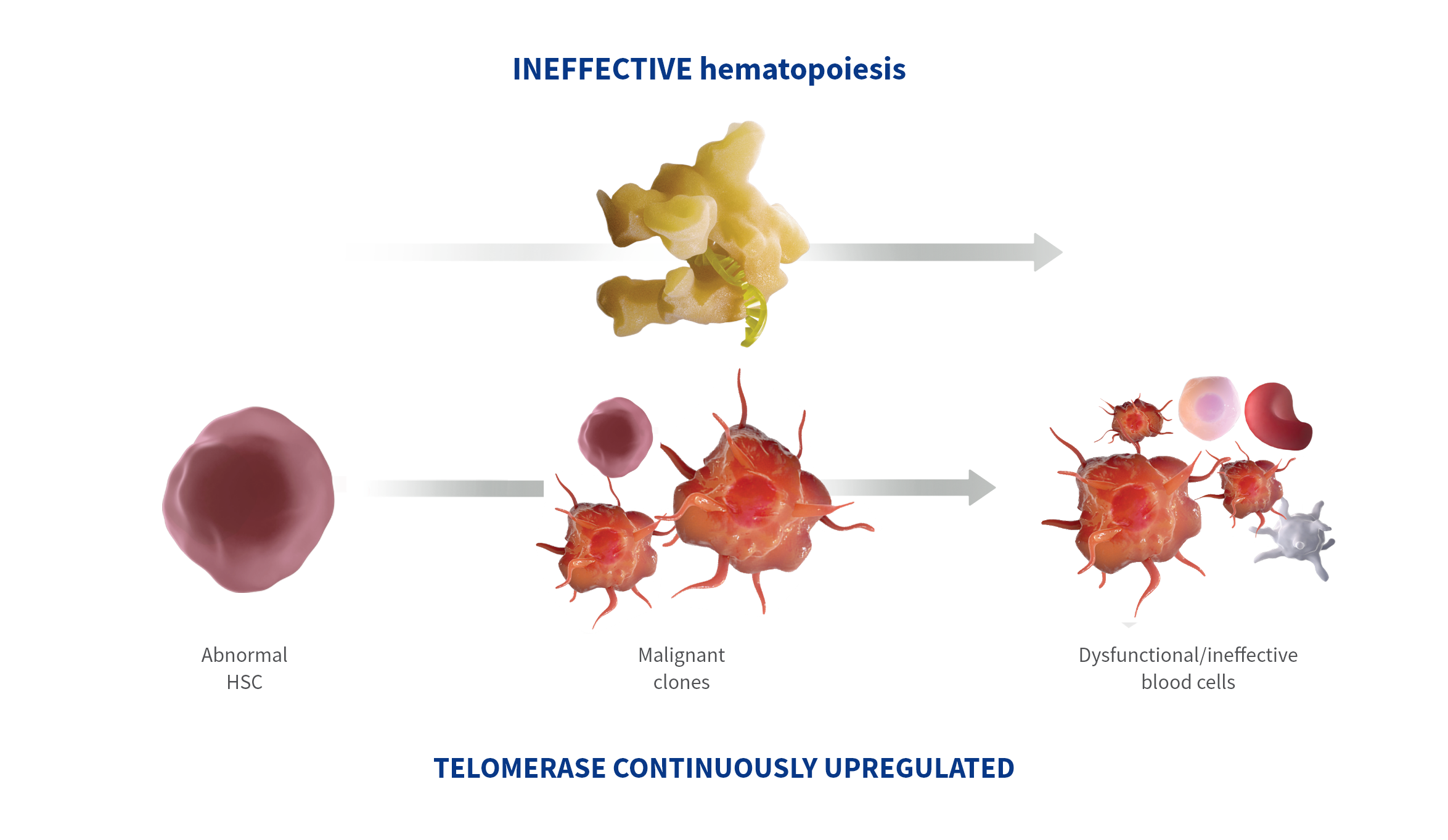
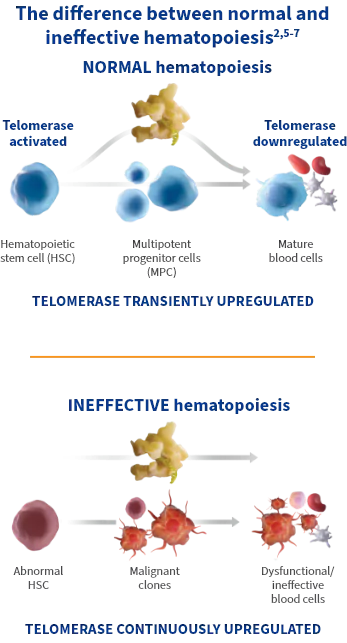
Abnormal and continuous upregulation of telomerase contributes to ineffective hematopoiesis1-3
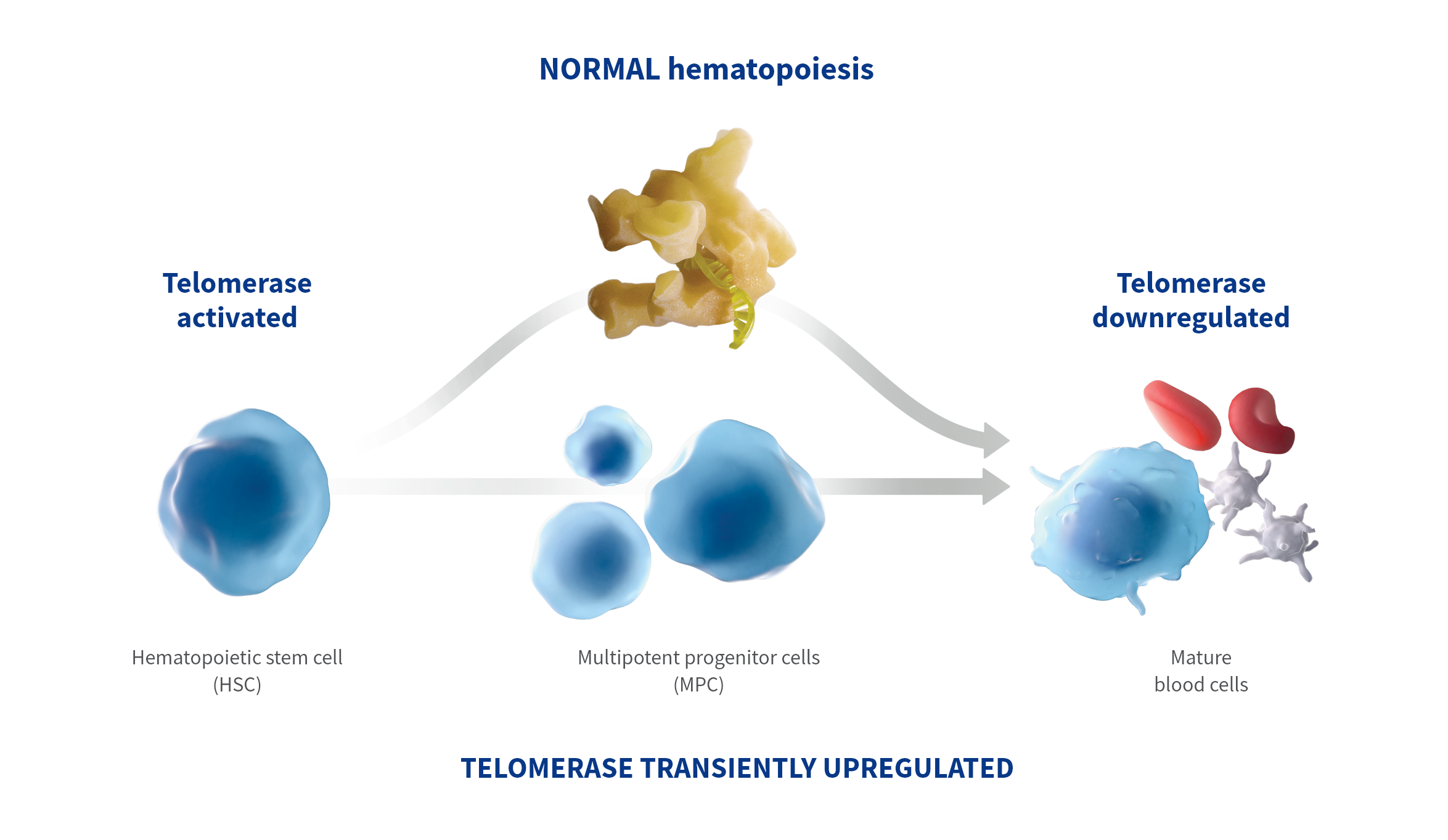
Telomerase is an enzyme that is upregulated in malignant cells and maintains telomere length.4
- Unlike most normal cells where telomerase activity is usually dormant, telomerase is transiently activated in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells during normal hematopoiesis5,6
- In malignant or dysfunctional cells, telomerase may be abnormally and continuously upregulated2
LR-MDS, lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes.
RYTELO is an oligonucleotide telomerase inhibitor that works differently from treatment options like ESAs, EMAs, or HMAs4
RYTELO targets telomerase4


Nonclinical studies showed imetelstat treatment led to4:
- Reduction of telomere length
- Reduction of malignant stem and progenitor cell proliferation
- Induction of apoptotic cell death
View the RYTELO mechanism of action video
EMA, erythroid-maturation agent; ESA, erythropoiesis-stimulating agent; HMA, hypomethylating agent.
References: 1. Shay JW. Role of telomeres and telomerase in aging and cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016;6(6):584-593. 2. Jafri MA, Ansari SA, Alqahtini MH, Shay JW. Roles of telomeres and telomerase in cancer, and advances in telomerase-targeted therapies. Genome Med. 2016;8(1):69. 3. Bruedigam C, Lane SW. Telomerase in hematologic malignancies. Curr Opin Hematol. 2016;23(4):346-353. 4. RYTELO. Prescribing information. Geron Corp.; 2024. 5. Hiyama E, Hiyama K. Telomere and telomerase in stem cells. Br J Cancer. 2007;96(7):1020-1024. 6. Yuan X, Larsson C, Xu D. Mechanisms underlying the activation of TERT transcription and telomerase activity in human cancer: old actors and new players. Oncogene. 2019;38(34):6172-6183. 7. Chapman J, Zhang Y. Histology, hematopoiesis. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; May 1, 2023. 8. Platzbecker U and Santini V, et al. Imetelstat in patients with lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes who have relapsed or are refractory to erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (IMerge): a multinational, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2024;403(10423):249-260.
INDICATION
RYTELO® (imetelstat) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with low- to intermediate-1 risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) with transfusion-dependent anemia requiring 4 or more red blood cell units over 8 weeks who have not responded to or have lost response to or are ineligible for erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESA).
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Thrombocytopenia
RYTELO® can cause thrombocytopenia based on laboratory values. In the clinical trial, new or worsening Grade 3 or 4 decreased platelets occurred in 65% of patients with MDS treated with RYTELO.
Monitor patients with thrombocytopenia for bleeding. Monitor complete blood cell counts prior to initiation of RYTELO, weekly for the first two cycles, prior to each cycle thereafter, and as clinically indicated. Administer platelet transfusions as appropriate. Delay the next cycle and resume at the same or reduced dose, or discontinue as recommended.
Neutropenia
RYTELO can cause neutropenia based on laboratory values. In the clinical trial, new or worsening Grade 3 or 4 decreased neutrophils occurred in 72% of patients with MDS treated with RYTELO.
Monitor patients with Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia for infections, including sepsis. Monitor complete blood cell counts prior to initiation of RYTELO, weekly for the first two cycles, prior to each cycle thereafter, and as clinically indicated. Administer growth factors and anti-infective therapies for treatment or prophylaxis as appropriate. Delay the next cycle and resume at the same or reduced dose, or discontinue as recommended.
Infusion-Related Reactions
RYTELO can cause infusion-related reactions. In the clinical trial, infusion-related reactions occurred in 8% of patients with MDS treated with RYTELO; Grade 3 or 4 infusion-related reactions occurred in 1.7%, including hypertensive crisis (0.8%). The most common infusion-related reaction was headache (4.2%). Infusion-related reactions usually occur during or shortly after the end of the infusion.
Premedicate patients at least 30 minutes prior to infusion with diphenhydramine and hydrocortisone as recommended and monitor patients for at least one hour following the infusion as recommended. Manage symptoms of infusion-related reactions with supportive care and infusion interruptions, decrease infusion rate, or permanently discontinue as recommended.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on animal findings, RYTELO can cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with RYTELO and for 1 week after the last dose.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 32% of patients who received RYTELO. Serious adverse reactions in >2% of patients included sepsis (4.2%), fracture (3.4%), cardiac failure (2.5%), and hemorrhage (2.5%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 0.8% of patients who received RYTELO, including sepsis (0.8%).
Most common adverse reactions (≥10% with a difference between arms of >5% compared to placebo), including laboratory abnormalities, were decreased platelets, decreased white blood cells, decreased neutrophils, increased AST, increased alkaline phosphatase, increased ALT, fatigue, prolonged partial thromboplastin time, arthralgia/myalgia, COVID-19 infections, and headache.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including Medication Guide.
You are encouraged to report adverse events related to Geron products by calling 1-855-437-6664 (1-855-GERON-MI) (US only). If you prefer, you may contact the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) directly. Visit www.fda.gov/MedWatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.